PainFingers are an indispensable sign of any common pathology in which the structural ingredients of these joints are damaged.First of all, pain in the area of these joints can be associated with various autoimmune diseases (Systematic red glow, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, etc.) in which immune factors cause damage to their articular tissue.
The other main reason that can startpainIn the finger joints, there may be injuries (Bruises, displacements, bone fractures, ligaments).Removal in these joints can also be provoked by degenerative changes that occur in their articular tissue.This can often be observed with osteoarthritis.
The anatomy of the hand joints
All hand joints are habit to be divided into the following groups:
- handwriting;
- wrist joints;
- Karpa model joints;
- Interrupt connections;
- Parlemonal -phalanx joints;
- Interfalanx links.
Wrist
Hand connection is formed by proximal bone bones (upper) a number of ankles (Trehedral, semi -mourn bone, scoken) and distal areas of radiation and elbow bone.The elbow bone is not directly connected to the wrist bones, but with the help of distal (Lower) articular disc.This structure separates the ankle cavity from the distal cavity (Lower) Tile joint.
Hand -knot
Handwalks are represented by three types of joints.The first form includes those joints that are between the upper bone (Scapoid, semi -munition, trehedral, peas) or lower row (in hook, head, head, trapezoidal, blocking bones).These joints are called interchange nodes.According to the second type, the so -called middle middle fusion is listed.This fusion has an S -shaped shape and is formed due to the bone bones of the upper and lower wrist row.The third type includes the joining of the pea bone.Through this knot, the trihedral bone is connected to the pea bone.
Chapter
Carpal panel connections connect the ankle bones and metacarpal bones.These joints are formed by the contact of the proximal edges (COUNTRY) Metacarpal bones and distal sections of carpal bones belonging to the second row.Carpal model connections include two main nodes.The first is the knot of the carpal game of the thumb.It is formed by the bond of the first metacarpal bone to the bone blockage.
The second connection is the usual union of carp sites for the rest of the carpal-prypyn compounds between the second, third, fourth, fifth metacarpal and trapezoidal bones, head bones and, in part, part of bone blockage.The connection of the carpal finger pattern is separated from the total knot of the carp model.Due to which the most active movements are possible in it, compared to the rest of the carp sites (which are included in the overall knot of the carp road) considered sedentary.Carpal panel connections are strengthened by strong articular capsules as well as ligaments (Palm and Palmar Ligaments).
Nodes
Side surfaces of the second, third, fourth and fifth metacarpal bones, when contacted by each other, form interprex joints.These joints have special articular capsules, which are approaching the joint capsules of the carpal path, are connected to them.In addition to the capsules, these joints have a ligamentous apparatus represented by inter -stern metacarpal ligaments, as well as posterior and palm ligaments.The intervention links are attributed to the sitting joints of the hand, as the articular bone surfaces that form these joints have a flat shape.
Parleen -phalanx nodes
Parleus-Falanx links are compounds between distal (lower) with the ends of the metacarpal and proximal bones (upper) areas of the first phalanges of the fingers of the hand.Each finger of the upper limbs has its metacarponal joint.Thus, there are five metacarpal counterparts from each hand.
Nodes interfalanx
Interpofalanx connections are formed by the combination of the neighboring phalanges of each of the fingers.Greatfirst) The finger has only one interpreted joint, as this finger has only two phalanxes (proximal and distal).The rest of the fingers of each of the hands have two interconnected joints.
The first of them is localized between the first (proximal) and second (average) fingers and are called proximal phalanges (upper) Interfalang union.The second forms the bond between the average (second) and last (distal) Finger phalanges.The second interphalangeal connections are called interpreted distal joints.Inter -phalalanx connections are strengthened with collateral and palm ligaments.These joints belong to the block joints, whose movements are only possible around the frontal plane (Fighting and bending).
What structures can be inflamed in the wrist joints?
Inflammation is a typical pathological process characteristic of those tissues and organs that were damaged for some reason.It is worth remembering that, in most cases, any disease (For example, gout, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.) or trauma that damage the wrist joints on one scale or another, affect not only the articular but also the perioster (Nerves, muscles, tendons, subcutaneous fat, skin) Structures.
The following articular structures can become inflamed in the wrist joints:
- joint cartilage;
- Squeezing bone tissue;
- joint capsule;
- Common ligaments.
Causes of pain in the joints of the hand and fingers
The main part among the reasons that cause pain in the joints of the hand and fingers is occupied by mechanical damage (Fractures, displacements, bruises, etc.) and systemic autoimmune diseases (Rheumatoid arthritis, systemic erythematosis of lupus, psoriasis, etc.).In addition to these causes, pain in the wrist joints can cause diseases associated with metabolic disorders (For example, gout, osteoarthrosis).
There are the following major causes that cause pain in the hand and fingers:
- hand and fingers;
- brush bone fracture;
- brush displacements;
- hand ligament lesion;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- Kinbek disease;
- reactive arthritis;
- gout;
- Psoriatic arthritis;
- synovitis;
- osteoarthrosis;
- The red lupus of the system.
Brushes of brushes and fingers
A bruising is one of the types of closed damage, in which there is a soft tissue damage (muscles, tendons, nerves, skin) And there is no wound in the place where the main action of the traumatic factor was directed.Bruises of soft tissue of hand and fingers are rarely found in isolation (MOREOVER) from the bruises of the joints of the hand and fingers.Therefore, with this type of injury, mixed symptoms are found, indicating both damage to the joints, and the periarticula lesion (periphery) fabrics.The brushes of the brush and fingers are usually found when they fall, damage it with an open object, with its compression or pinching.
Very often, the cystic area bruises lead to damage to the main drawers of the medium nerves, radial, elbow (which interior area of hand and fingers), which is immediately manifested by the loss of skin sensitivity, and in some cases the disappearance of motor functions of the fingers.
Inflammatory edema of the articular and permeable structures develops as a result of the expansion of multiple vessels than they are blood supply.This edema is one of the reactions of inflammation, which occurs in response to tissue damage during bruises.
A brush fracture of the brush
Very often, the cause of pain in the hand joints can be different fractures of its bones, as these bones are directly recorded in the formation of articular surfaces.Depending on the anatomical position of the damaged bone, all fractures are divided into three main groups.The first group includes ankle bone fractures.The second includes tubular metacarpale bone fractures.The third group includes finger fractures of the fingertips.
The most common places of damage to the brush carpal area are semi -mammary bones and schedhoids.A fracture of these bones occurs while falling into the brush and is associated with pain in the ankle area and medium joints.Pain syndrome can also be observed at the anatomical localization of these bones.
The most common fracture of the metacarpal bone ends is a fracture of the first metacarpal bone base (what is glued to the phalanges of the bone of the thumb).With this injury, edema and pain appear in the area of the first metatarsal bone base, as well as in that part of the fusion of the carpal model, which directly adjacent to it.The thumb with such a fracture is cut, bent and led to the palm of the hand.His movements are limited.
The phalanx fractures of the brush are associated with deformation, a decrease in fingertips, loss of their function, sharp pain and swelling in their inter -phalang joints and peri -inhuman tissue.With fractures of the finger phalanges with a displacement of bone fragments, palpation (palpation) You can identify their swelling on the surface of the brush palm, and on the back, on the contrary, a hole or insulation.These fragments are usually mobile, close to them you can often detect subcutaneous bleeding (hematoma).
The brush shift
Displacement is a pathological condition in which bone areas that form each union go beyond its anatomical boundaries, which, thus, are manifested by a complete or partial loss of the function of this union.In addition to the damaged function of the joints during displacements, severe pain in the affected joint, swelling and a local temperature rise are also found.During the brush displacement, the occurrence of swelling is explained not only by the presence of inflammation in the damaged peri -inhuman tissue, as well as the joint structures, but also with an extension of the bone joint.
The most common types of brush displacements
| Name of displacement | Mechanism of displacement | Which union is amazed? |
| True brush displacement | The articular surfaces of the ankle bones are moved in conjunction with the surface of the radial bone joint toward the palm or the back of the hand. |
|
| Perilunare | The wrist bones and the rest of the brush are moved compared to the noon and radial bone at the back of the brush. |
|
| Bone displacement | At the same time, the scoken bone indicates the displacement on the side of the radiation in parallel (on the same plane) in nearby hand ankle bones.Sometimes it can be moved to the palm side, that is, pass to the palm of the bone blockage, less often on the same side of the trapezoidal bone. |
|
| Half -monitor displacement | There is a slide of half of the denial in the direction of the palm so that the space at the site of this bone remains not busy.It is gradually occupied by the head bone, penetrating here from the second row of the ankle bones.This displacement is a complication of itself -perilunar displacement regulation. |
|
| Metacarpal first bone displacement | The articular surface of the base of the first metacarpale bone is moved in conjunction with the articular surface of the bone blockage on the side of the radiation, up (above (proximal) and on the same plane with the wrist bones.Thus, the thumb is pulled slightly back and toward the wrist joint. |
|
| The shift of phalanges of fingers | There is finger displacement in the metacarpophalangeal joints and cross-back joints.In the first, the common surface of the proximal phalaranx of the fingers (Along with the whole finger) moves in relation to the articular surface of the metacarpal bones.With the second, there is a shift between the bones of the phalanges of the finger itself.Usually there are returns and displacement of the finger phalanges palm. |
|
Damage to hand ligaments
The lesion of the ligaments along with the brush bruises is attributed to the closed traumatic damage.This pathology is mainly found with excessive wrist extension, fingers in each direction.The main types of brush band lesions are their extension and rupture.With the extension in the damage area, the new tension and partial rupture of the connective tissue fibers are observed.With the rupture of the ligaments, the whole ligament is divided into two endless ends.
The following main types of brush ligament fractures are distinguished:
- rupture of the carpal radial collateral ligament;
- rupture of the ankle elbow collateral;
- rupture of wiretapping ligaments;
- rupture of the lateral ligaments of the metacarpal counterpart joints;
- Rupture of the lateral ligaments of the interphalang joints.
Rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease in which the human immune system damages its body tissues.In other words, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune pathology.This disease is also systemic, as many tissues are affected with (Muscles, joints, vessels, etc.) and the organs (Heart, kidneys, lungs, etc.) in the body.
Despite the fact that rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic disease underneath, to a greater extent, the joints suffer, while the lesion of other tissues and organs is in the background.With this disease, almost all types of brush joints can be affected (Handcuffs, carpal citizen, metakarpal -phalanx, cross-director nodes).The lesion is usually symmetrical (They the same nodes are affected) In both hands, accompanied by swelling, pain in damaged joints.In the morning, during the bed, there is some stiffness in the affected joints, which can last about 1 hour and then disappear without trace.
Very often with rheumatic arthritis near the affected brush joints (Most often piano-Çalanx joints, cross-directors) Rheumatoid joints appear.They are a rounded lineup located under the skin.In the brush, these formations arise most often on the back.In palpation, they are dense, inactive, painless.Their number can change.
Cin -disease
Kinbek's disease is a pathology in which a half -denied brush carpal bone is affected.The disease develops as a result of the long -term physical overload of the palms of the hands.It usually occurs in specialists in construction occupations - plaster, mason, coupling, etc.Excessive physical activity of palm palms most often this bone, as it occupies the central position in the first ankle.Most often, during Kinbek's disease, the brush of one side is affected and, as a rule, the main one (Right hand is damaged, left hand is damaged).
Reactive arthritis
Reactive arthritis is a pathology of immunopathological genesis, in which its immune system attacks different joints in the body, which is why autoimmune inflammation develops.Unlike other autoimmune diseases (For example, rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, in which an infectious origin is assumed) In reactive arthritis, a clear relationship between infection (and, in particular, intestines or urogenital) and the development of common lesions.
Also, with this pathology, the lymph nodes can grow and appear fever.When the passage of reactive arthritis into a chronic form, over time, patients may show signs of kidney, heart and muscle atrophy, can occur bursitis (Inflammation of periosenantal bags), Tendovaginites (Inflammation of the vagina of tendons) and others.
gout
Gout is a disease based on the development of accumulation of uric acid in the body and its deposition in the form of salts in the joints.Uralgic acid is the final product of metabolism of purine and pyrimidine bases.They serve as the basis for building DNA and RNA molecules, some power formations (Adenosine trifosfate, adenosine monophosphate, etc.) and vitamins.
Gout pain mainly occurs in the small joints of the lower and upper extremities.Moreover, in 50% of all clinical cases, the disease begins with the first plus union of feet.In the hands, as a rule, the interpreted finger joints are affected, less often - radiant joints.The use usually damages one or more joints in one limb, sometimes the joints of the other limbs are involved in the inflammatory process.
Psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a pathology in which different joints are inflamed against the background of psoriasis.The development of psoriasis is based on a violation of the interaction between immune cells and skin cells as a result of which in the body (and especially on the skin) There are autoimmune reactions that cause inflammation.
SINOVI
Synovitis is an inflammation of the synovial shell of the joints, associated with damage to its tissue and accumulation of pathological fluid in the affected joints.Synovitis is not a special disease, but on the contrary it serves as a complication of other diseases.It can occur with endocrine, allergic, infectious, autoimmune pathology, brushes, etc.
Osteoarthrosis
Osteoarthritis is a disease in which there is a violation of the processes of normal cartilage tissue in different joints.These processes have been violated under the influence of several external and internal predisposing factors.They can be constant joint damage, prolonged physical activity (At work, in everyday life, during the sport), inheritance, other common diseases, etc.
Finger connections are sore with this pathology because in the periarticular (periphery) Tissues occur inflammation, the nerves are affected.A characteristic feature of osteoarthritis is the association of pain with physical activity.Pain in the joints mainly appears in the and/or after severe physical overload and disappears at rest or after rest.
The red lupus of the system
A systemic lupus erythematosus is an autoimmune pathology, in which in the human body there is a production of an immune system of autoimmune antibodies, attacking different structures of cells and tissues.In particular, with it, there is the production of so -called anti -core antibodies that damage the cell nuclei and DNA and RNA molecules.With a red lupus, various fabrics and organs - leather, boat, heart, pleura, pericardium, kidney, joints, etc. are affected.
The red lupus of the system is constantly associated with other extra signs of inaccessible - weakness, weight loss, fever (Improving body temperature).However, special symptoms are of greater importance, without which the red lupus is not diagnosed.These special signs are photodermatitis (Inflammation of the skin under the influence of sunlight), discooid rash (The view on the neck of the neck, the red papal chest), lupoid butterfly (The appearance of red spots on the skin near the nose), erosion in the oral cavity, kidney damage (Glomerulonephritis), Seroses (Inflammation of serous membranes) and others.
Diagnosis of causes of pain pain
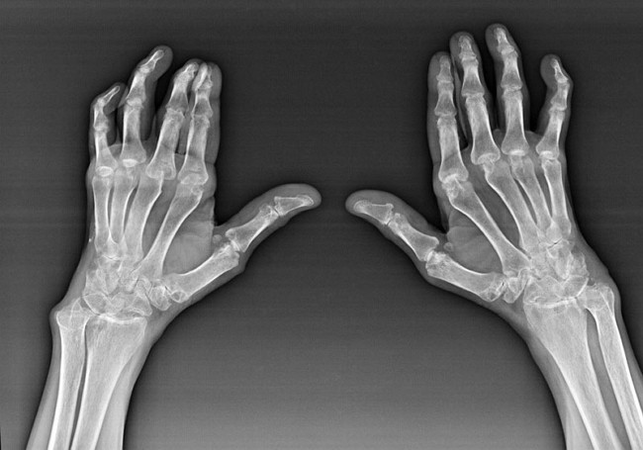
Hands of pain in the hand joints are engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of causes of pain, mainly a traumatologist and physician for growing A. to diagnose such reasons, these doctors use mainly clinical (Anamnesis collection, external inspection, palpation, etc.), radial (Radiography, calculated tomography) and laboratory (General blood test, biochemical blood test, etc.) Research methods.
Depending on the cause of the pain in the hand joints, all diagnostics can be divided into the following sections:
- Diagnosis of traumatic brush injuries (bruises, displacements, fractures, ligaments);
- Diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis;
- Diagnosis of Kinbek disease;
- Diagnosis of reactive arthritis;
- Gout diagnostics;
- Diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis;
- Diagnosis of synovitis;
- Diagnosis of osteoarthrosis;
- Diagnosis of systemic lupus erythematosis.
Diagnosis of traumatic brush injuries
When brush injuries, you should consult a traumatologist.The main methods of diagnosis used in medical practice to identify traumatic brush damage (Fractures, displacements, ligaments, bruises), are an external examination, anamnesis, search radiation methods (Radiography, calculated tomography).
The collection of anamnestic data allows the physician to identify incidents that led or may lead to a brush injury.The history of anamnesis is also used to clarify the symptoms that concern the patient.During an external examination in the brush, it is possible to detect swelling, hematomas, its deformity, restriction of joint mobility.With the help of palpation, the doctor detects the presence of pain, violation of the anatomical shape of the joint, damage to the ligaments.Search radiation methods (Radiography, calculated tomography) They allow you to confirm the diagnosis, as during their use, the mechanical damage to the anatomical brush formations is clearly visible.
Treatment of pathologies that cause inflammation of the hand joints
For the treatment of the causes of pain in the joints of the hand and fingers, doctors, first of all, prescribe a variety of medicines (Anti -inflammatory, soothing soothing, anti -rrevetas drugs, etc.).In some cases, they combine the use of these products with physiotherapeutic procedures.Traumatic brush damage is most often treated surgical or applied to the affected upper limb of the gypsum bandage.
To relieve pain and relieve inflammation, first aid may be the use of an external NSAID.The drug selectively blocks COO-2 and acts directly on the source of pain.It is absorbed quickly thanks to a special quality, leaves no trace of clothes, has a pleasant smell.
Depending on the pathology that causes inflammation in the hand joints, the entire treatment can be divided into the following parts:
- Treatment of traumatic brush injuries (bruises, displacements, fractures, ligaments);
- treatment of rheumatoid arthritis;
- Treatment of Kinbek disease;
- treatment of reactive arthritis;
- Treatment of gout;
- treatment of psoriatic arthritis;
- treatment of synovitis;
- treatment of osteoarthritis;
- Treatment of systemic erythematosis of the lupus.